Dictionary box
Term
Definition
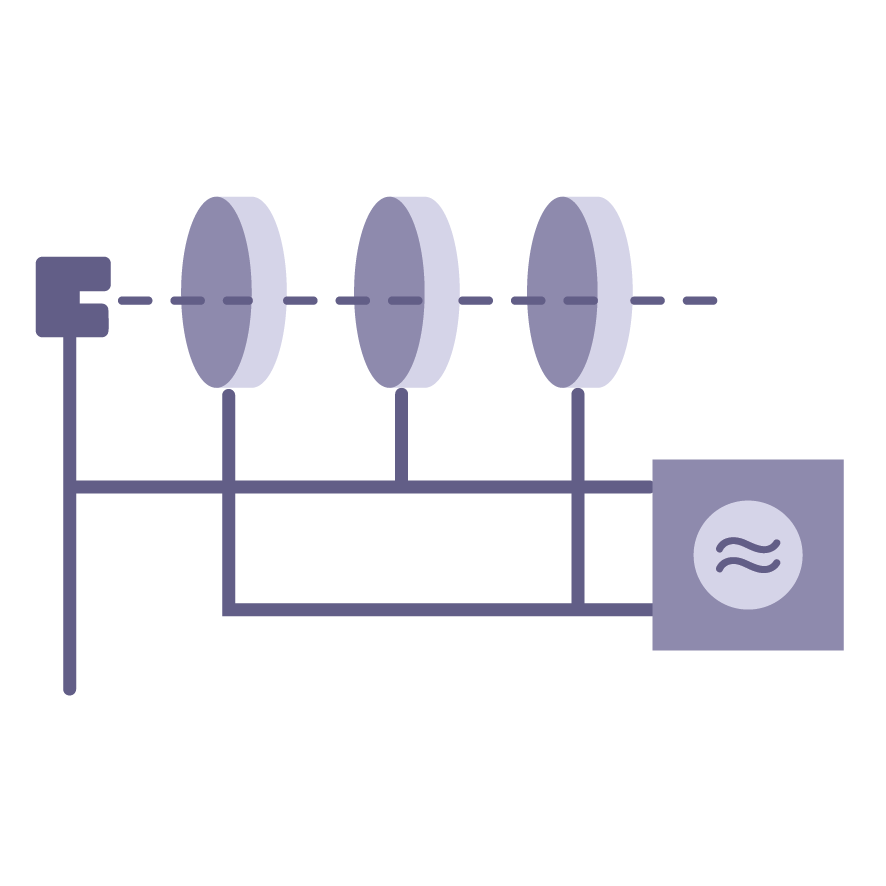
LINAC (Linear Accelerator)
A machine that accelerates electrons in a straight line using high-energy electromagnetic fields. In medicine, it is mainly used for precise cancer radiation therapy and can also be adapted to produce medical isotopes.
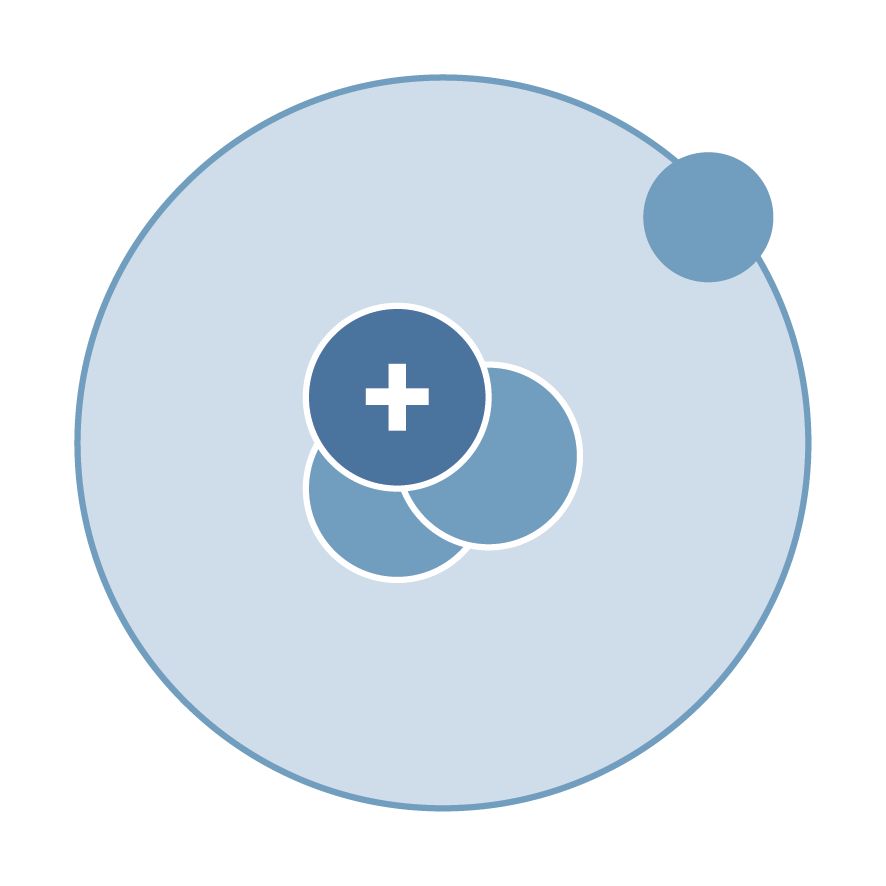
Radioisotope
A radioactive form of a chemical element that emits radiation as it decays. Radioisotopes are essential in medicine for imaging, diagnosis, and therapy, serving as the base materials for radiopharmaceuticals. Also named radionuclide.
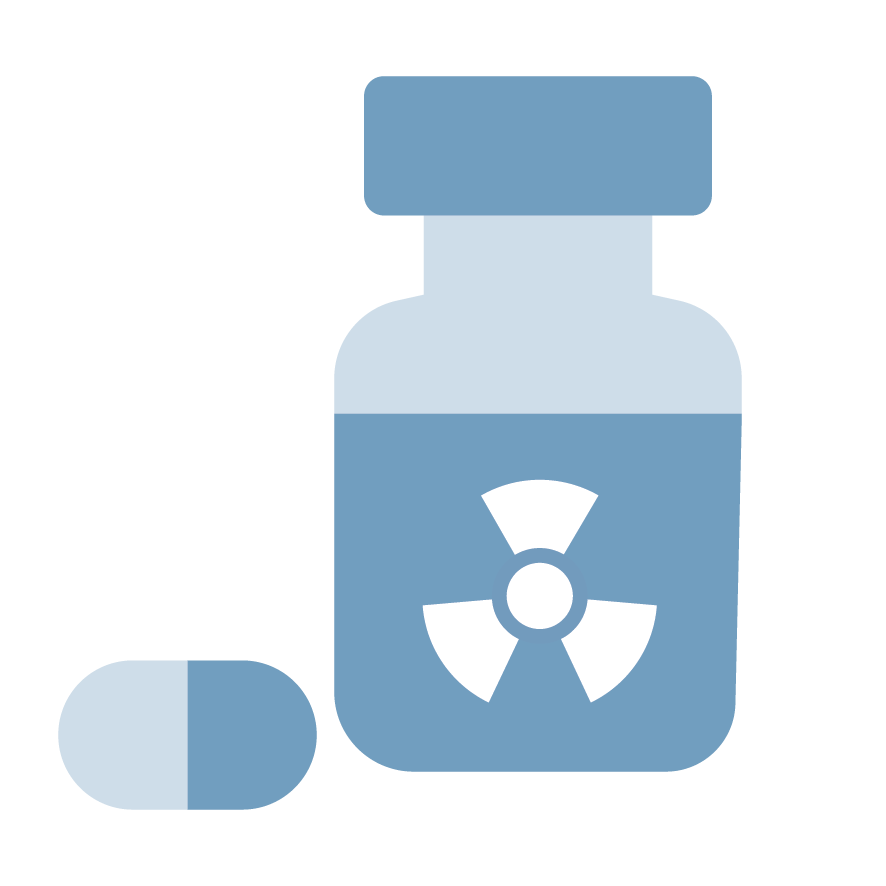
Radiopharmaceutical
A medicinal product that combines a radioisotope with a biological molecule to target specific tissues or organs. Used for diagnostic imaging (e.g., PET scans) and therapeutic applications (e.g., targeted cancer treatments).

Theranostics
A medical approach that combines therapy and diagnostics in one process, using radiopharmaceuticals to both detect disease and deliver targeted treatment, often in cancer care.

Cyclotron
A type of particle accelerator that produces certain radioisotopes by bombarding stable atoms with charged particles. Cyclotrons are widely used for generating isotopes such as Fluorine-18 for PET imaging.
Nuclear Reactor
A facility where controlled nuclear fission reactions occur, traditionally used to produce large quantities of medical radioisotopes (e.g., Molybdenum-99). Many reactors in use today are aging, creating supply challenges.